Piezoceramic Solutions for High-Intensity Focused Ultrasound
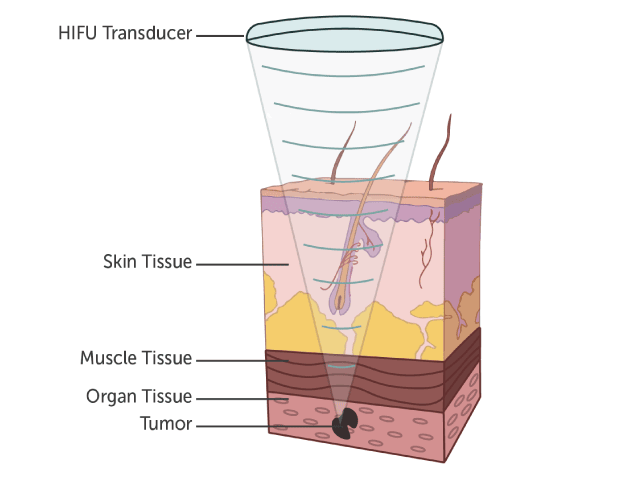
The use of medical ultrasound has increased substantially in recent years, driven in part by the expansion of the technology from diagnostic medicine to the therapeutic field. Focused ultrasound is now being used for several forms of medical treatment including minimally invasive and non-invasive surgery and dermatological procedures.
High-intensity focused ultrasound (HIFU) offers medical practitioners an efficient and effective method of treating various conditions without harming the body tissue in the process. Applications range from shallow skin tissue rejuvenation over treatment of neurological disorders such as essential tremor to the ablation of early stage tumors.
How does HIFU work?
HIFU equipment commonly utilizes a piezoelectric transducer to generate ultrasonic waves in the 1-20 MHz range by means of the converse piezoelectric effect. The ultrasonic energy is focused on a pinpointed location to affect the tissue either mechanically or thermally. In general, there are two methods of focusing ultrasounic waves onto a specific target:
Focusing Bowls
A common HIFU transducer set-up employs a focusing bowl, typically made of a piezoelectric ceramic material, that will concentrate ultrasonic energy onto a pinpointed location, not unlike the way a magnifying glass concentrates sunlight. The ultrasonic energy will penetrate the surrounding tissue without harming it, only reaching full intensity at the point of convergence.

Phased Arrays
Alternatively, a HIFU transducer can be constructed with multiple piezoceramic plates positioned in so-called phased arrays. These transducer designs allow operators to stir the focus without moving the array itself and can enable the generation of multiple foci simultaneously.
Smaller transducers called linear arrays can be inserted into body cavities to emit ultrasonic energy internally to for instance dissolve a blood clot or stimulate muscle recovery. Larger, two-dimensional arrays are instead used for extracorporeal radiation.
CTS capabilities for HIFU transducers
CTS piezoceramic focusing bowls and plates can be customized according to our customers exact dimensional and performance requirements and can be manufactured in production volumes. The dimensional ranges for these particular products can be viewed in the tables below:
| Bowl Properties |
Unit |
Range |
| Outer Diameter (OD) |
mm |
3-65 |
| Thickness (Th) |
mm |
0.1-2 |
| Radius of Curvature |
mm |
Down to OD/2 |
| Frequency |
MHz |
1-20 |
| Plate Properties |
Unit |
Range |
| Length (L) |
mm |
0.4-150 |
| Width (W) |
mm |
1.5-100 |
| Thickness (Th) |
mm |
0.076-25 |
| Frequency |
MHz |
0.5-25 |
CTS has developed several piezoceramic material formulations specifically for HIFU use. These materials are of the ‘hard’ PZT type, charaterized by having very high coupling factors and low dielectric and mechanical losses for maximal acoustic energy output. Our Pz26 ceramic can be used as a direct replacement for all Navy I materials and is a solid choice for most HIFU applications. For highly specialized HIFU transducers requiring lower electrical impedance, the Pz50 series provides even higher permittivities and piezoelectric coefficients. All materials show great stability over time and temperature, displaying some of the lowest aging rates in the industry.
| Properties |
Symbol |
Unit |
Value |
| Recommended PZT Material |
- |
- |
Pz26 |
Pz52 |
Pz54 |
| Ideal Power Range |
- |
- |
High Power ⇔ Low Power |
| Electrical Impedance Range |
- |
- |
High Electrical Impedance ⇔ Low Electrical Impedance |
| Relative Free Dielectric Constant (1kHz) |
K33σ |
- |
1300 |
1900 |
2800 |
| Dielectric Dissipation Factor (1kHz) |
tanδ |
|
0.003 |
0.003 |
0.003 |
| Curie Temperature |
TC |
°C |
330 |
235 |
220 |
| Mechanical Quality Factor |
Qm |
- |
>1000 |
550 |
1500 |
| Coupling Coefficient |
kt |
- |
0.47 |
0.53 |
0.48 |
| Coupling Coefficient |
k33 |
- |
0.68 |
0.7 |
0.7 |
Piezoelectric Charge Coefficient
(Displacement Coefficient) |
d33 |
pC/N |
300 |
440 |
460 |
Customization and value-add for transducers
Each company that CTS partners with has unique needs that require custom solutions. Our team of engineers work directly with customers, designing solutions that meet demanding specifications. Typical customizations and value-add opportunities for focusing bowls and plates in HIFU applications are:
Tolerances: Components can be manufactured with tight tolerances, both in terms of geometry and functionality (e.g. frequency), in order to provide precise focusing of the ultrasonic beam.
Electrode shaping: In place of standard plain electrodes, CTS can print wrap-around electrodes, allowing for both electric contacts to be placed on the same side.
Transducer assembly and testing: CTS has extensive processing capabilities and can offer wiring, coating and transducer assembly, providing a sub-system to facilitate integration in the final application. We also perform testing of transducers under customer-specified operating conditions with full traceability of test results.